Java Aes 128 Key Generator
Jul 06, 2016 Given a message, We would like to encrypt & decrypt plain/cipher text using AES CBC algorithm in java. We will perform following operations: Generate symmetric key using AES-128.; Generate initialization vector used for CBC (Cipher Block Chaining).; Encrypt message using symmetric key and initialization vector.; Decrypt the encrypted message using symmetric key and initialization. Sep 04, 2018 AES supports key lengths of 128, 192 and 256 bit. AES comprises of 3 block ciphers AES-128, AES-192 and AES-256, each cipher encrypts and decrypts the data in the block of 128 bits using the secret key of 128, 192 and 256 bits respectively.
Note
No new features or functionality are being added to Media Services v2.
Check out the latest version, Media Services v3. Also, see migration guidance from v2 to v3
You can use Media Services to deliver HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Smooth Streaming encrypted with the AES by using 128-bit encryption keys. Media Services also provides the key delivery service that delivers encryption keys to authorized users. If you want Media Services to encrypt an asset, you associate an encryption key with the asset and also configure authorization policies for the key. When a stream is requested by a player, Media Services uses the specified key to dynamically encrypt your content by using AES encryption. To decrypt the stream, the player requests the key from the key delivery service. To determine whether the user is authorized to get the key, the service evaluates the authorization policies that you specified for the key.
If google play gift card is a bad idea from the beginning, surely you will not find it anymore today, right? Free google gift card generator. But it is still popular, not only in United States, but worldwide.
Media Services supports multiple ways of authenticating users who make key requests. The content key authorization policy can have one or more authorization restrictions, either open or token restrictions. The token-restricted policy must be accompanied by a token issued by a security token service (STS). Media Services supports tokens in the simple web token (SWT) and JSON Web Token (JWT) formats. For more information, see Configure the content key's authorization policy.
To take advantage of dynamic encryption, you need to have an asset that contains a set of multi-bitrate MP4 files or multi-bitrate Smooth Streaming source files. You also need to configure the delivery policy for the asset (described later in this article). Then, based on the format specified in the streaming URL, the on-demand streaming server ensures that the stream is delivered in the protocol you selected. As a result, you need to store and pay only for the files in single storage format. Media Services builds and serves the appropriate response based on requests from a client.
This article is useful to developers who work on applications that deliver protected media. The article shows you how to configure the key delivery service with authorization policies so that only authorized clients can receive encryption keys. It also shows how to use dynamic encryption.
For information on how to encrypt content with the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for delivery to Safari on macOS, see this blog post.For an overview of how to protect your media content with AES encryption, see this video.
AES-128 dynamic encryption and key delivery service workflow
Perform the following general steps when you encrypt your assets with AES by using the Media Services key delivery service and also by using dynamic encryption:
Create an asset, and upload files into the asset.
Encode the asset that contains the file to the adaptive bitrate MP4 set.
Create a content key, and associate it with the encoded asset. In Media Services, the content key contains the asset's encryption key.
Configure the content key's authorization policy. You must configure the content key authorization policy. The client must meet the policy before the content key is delivered to the client.
Configure the delivery policy for an asset. The delivery policy configuration includes the key acquisition URL and an initialization vector (IV). (AES-128 requires the same IV for encryption and decryption.) The configuration also includes the delivery protocol (for example, MPEG-DASH, HLS, Smooth Streaming, or all) and the type of dynamic encryption (for example, envelope or no dynamic encryption).
You can apply a different policy to each protocol on the same asset. For example, you can apply PlayReady encryption to Smooth/DASH and an AES envelope to HLS. Any protocols that aren't defined in a delivery policy are blocked from streaming. (An example is if you add a single policy that specifies only HLS as the protocol.) The exception is if you have no asset delivery policy defined at all. Then, all protocols are allowed in the clear.
Create an OnDemand locator to get a streaming URL.
The article also shows how a client application can request a key from the key delivery service.
Java Aes 128 Key Generator Manual
You can find a complete .NET example at the end of the article.
The following image demonstrates the workflow previously described. Here, the token is used for authentication.
The remainder of this article provides explanations, code examples, and links to topics that show you how to achieve the tasks previously described.
Current limitations
If you add or update your asset's delivery policy, you must delete any existing locator and create a new locator.
Create an asset and upload files into the asset
To manage, encode, and stream your videos, you must first upload your content into Media Services. After it's uploaded, your content is stored securely in the cloud for further processing and streaming.
For more information, see Upload files into a Media Services account.
Encode the asset that contains the file to the adaptive bitrate MP4 set
With dynamic encryption, you create an asset that contains a set of multi-bitrate MP4 files or multi-bitrate Smooth Streaming source files. Then, based on the specified format in the manifest or fragment request, the on-demand streaming server ensures that you receive the stream in the protocol you selected. Then, you only need to store and pay for the files in single storage format. Media Services builds and serves the appropriate response based on requests from a client. For more information, see Dynamic packaging overview.
Note
When your Media Services account is created, a default streaming endpoint is added to your account in the 'Stopped' state. To start streaming your content and take advantage of dynamic packaging and dynamic encryption, the streaming endpoint from which you want to stream content must be in the 'Running' state.
Also, to use dynamic packaging and dynamic encryption, your asset must contain a set of adaptive bitrate MP4s or adaptive bitrate Smooth Streaming files.
For instructions on how to encode, see Encode an asset by using Media Encoder Standard.
Create a content key and associate it with the encoded asset
In Media Services, the content key contains the key that you want to encrypt an asset with.
For more information, see Create a content key.
Configure the content key's authorization policy
Media Services supports multiple ways of authenticating users who make key requests. You must configure the content key authorization policy. The client (player) must meet the policy before the key can be delivered to the client. The content key authorization policy can have one or more authorization restrictions, either open, token restriction, or IP restriction.
For more information, see Configure a content key authorization policy.
Configure an asset delivery policy
Configure the delivery policy for your asset. Some things that the asset delivery policy configuration includes are:
Java Aes 128 Key Generator Software
- The key acquisition URL.
- The initialization vector (IV) to use for the envelope encryption. AES-128 requires the same IV for encryption and decryption.
- The asset delivery protocol (for example, MPEG-DASH, HLS, Smooth Streaming, or all).
- The type of dynamic encryption (for example, AES envelope) or no dynamic encryption.
For more information, see Configure an asset delivery policy.
Create an OnDemand streaming locator to get a streaming URL
You need to provide your user with the streaming URL for Smooth Streaming, DASH, or HLS.
Note
If you add or update your asset's delivery policy, you must delete any existing locator and create a new locator.
For instructions on how to publish an asset and build a streaming URL, see Build a streaming URL.
Get a test token
Get a test token based on the token restriction that was used for the key authorization policy.
You can use the Azure Media Services Player to test your stream.
How can your client request a key from the key delivery service?
In the previous step, you constructed the URL that points to a manifest file. Your client needs to extract the necessary information from the streaming manifest files to make a request to the key delivery service.
Manifest files
The client needs to extract the URL (that also contains content key ID [kid]) value from the manifest file. The client then tries to get the encryption key from the key delivery service. The client also needs to extract the IV value and use it to decrypt the stream. The following snippet shows the <Protection> element of the Smooth Streaming manifest:
In the case of HLS, the root manifest is broken into segment files.
For example, the root manifest is: http://test001.origin.mediaservices.windows.net/8bfe7d6f-34e3-4d1a-b289-3e48a8762490/BigBuckBunny.ism/manifest(format=m3u8-aapl). It contains a list of segment file names.
If you open one of the segment files in a text editor (for example, http://test001.origin.mediaservices.windows.net/8bfe7d6f-34e3-4d1a-b289-3e48a8762490/BigBuckBunny.ism/QualityLevels(514369)/Manifest(video,format=m3u8-aapl), it contains #EXT-X-KEY, which indicates that the file is encrypted.
Note
If you plan to play an AES-encrypted HLS in Safari, see this blog.
Request the key from the key delivery service
The following code shows how to send a request to the Media Services key delivery service by using a key delivery Uri (that was extracted from the manifest) and a token. (This article doesn't explain how to get SWTs from an STS.)
Protect your content with AES-128 by using .NET
Create and configure a Visual Studio project
Set up your development environment, and populate the app.config file with connection information, as described in Media Services development with .NET.
Add the following elements to appSettings, as defined in your app.config file:
Example
Overwrite the code in your Program.cs file with the code shown in this section.
Note
There is a limit of 1,000,000 policies for different Media Services policies (for example, for Locator policy or ContentKeyAuthorizationPolicy). Use the same policy ID if you always use the same days/access permissions. An example is policies for locators that are intended to remain in place for a long time (non-upload policies). For more information, see the 'Limit access policies' section in Manage assets and related entities with the Media Services .NET SDK.
Make sure to update variables to point to folders where your input files are located.
Media Services learning paths
Media Services v3 (latest)
Check out the latest version of Azure Media Services!
Media Services v2 (legacy)

Provide feedback
Use the User Voice forum to provide feedback and make suggestions on how to improve Azure Media Services. You also can go directly to one of the following categories:
Advanced Encryption Standard(AES) is a symmetric encryption algorithm. AES is the industry standard as of now as it allows 128 bit, 192 bit and 256 bit encryption.Symmetric encryption is very fast as compared to asymmetric encryption and are used in systems such as database system. Following is an online tool to generate AES encrypted password and decrypt AES encrypted password. It provides two mode of encryption and decryption ECB and CBC mode. For more info on AES encryption visit this explanation on AES Encryption.
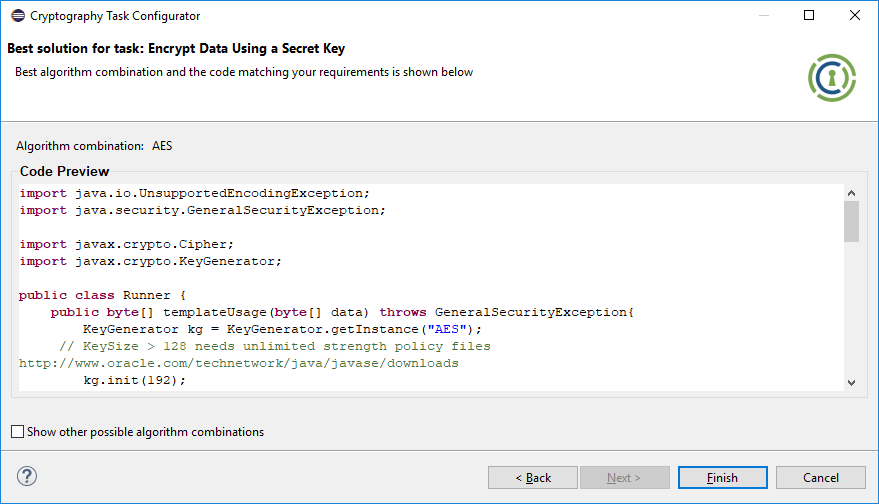
Also, you can find the sample usage screenshot below:
If You Appreciate What We Do Here On Devglan, You Can Consider:
- Like us at: or follow us at
- Share this article on social media or with your teammates.
- We are thankful for your never ending support.
Usage Guide
Any plain-text input or output that you enter or we generate is not stored on this site, this tool is provided via an HTTPS URL to ensure that text cannot be stolen.
For encryption, you can either enter the plain text, password, an image file or a .txt file that you want to encrypt. Now choose the block cipher mode of encryption. ECB(Electronic Code Book) is the simplest encryption mode and does not require IV for encryption. The input plain text will be divided into blocks and each block will be encrypted with the key provided and hence identical plain text blocks are encrypted into identical cipher text blocks. CBC mode is highly recommended and it requires IV to make each message unique. If no IV is entered then default will be used here for CBC mode and that defaults to a zero based byte[16].
The AES algorithm has a 128-bit block size, regardless of whether you key length is 256, 192 or 128 bits. When a symmetric cipher mode requires an IV, the length of the IV must be equal to the block size of the cipher. Hence, you must always use an IV of 128 bits (16 bytes) with AES.
AES provides 128 bit, 192 bit and 256 bit of secret key size for encryption. Things to remember here is if you are selecting 128 bits for encryption, then the secret key must be of 16 bits long and 24 and 32 bits for 192 and 256 bits of key size. Now you can enter the secret key accordingly. By default, the encrypted text will be base64 encoded but you have options to select the output format as HEX too.
Similarly, for image and .txt file the encrypted form will be Base64 encoded.
Below is a screenshot that shows a sample usage of this online AES encryption tool.
AES decryption has also the same process. By default it assumes the entered text be in Base64. The input can be Base64 encoded or Hex encoded image and .txt file too. And the final decrypted output will be Base64 string. If the intended output is a plain-text then, it can be decoded to plain-text in-place.
But if the intended output is an image or .txt file then you can use this tool to convert the base64 encoded output to an image.
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.