Python Add Generated Key And Value To Dictionary
Add a key:value pair to dictionary in Python Dictionary in Python is an unordered collection of data values, used to store data values like a map, which unlike other Data Types that hold only single value as an element, Dictionary holds key:value pair.
- May 02, 2017 This video shows how to add an item to a Python dictionary and at the same time introduces typical terminology used when talking about dictionaries. Adding a Key Value Item to a Python.
- Python Program to Create Dictionary of keys and values are square of keys Example 1. In this python program we are using using for loop to iterate from 1 to user specified value. Within the Python for loop, we are assigning values for Dictionary by using exponent operator.
- Jun 01, 2019 Python provides one keys method to get all keys from a python dictionary. Then we can iterate through the keys one by one and print out the value for each key. Then we can iterate through the keys one by one and print out the value for each key.
- We will demonstrate how the Python dictionaries are created in Python and how remove or add items into the Python dictionary. We will also discuss a number of Python methods that can be used with Python dictionary. A Python dictionary can be considered as the unordered collection of the items. A dictionary consists of a key and a value as pair.
- In Python, the Dictionary data types represent the implementation of hash tables. The Keys in the dictionary satisfy the following requirements. The keys of the dictionary are hashable i.e. The are generated by hashing function which generates unique result for each unique value supplied to the hash function. The order of data elements in a.
Dictionary
A dictionary is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. In Python dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and they have keys and values.
Example
Create and print a dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
print(thisdict)
Accessing Items
You can access the items of a dictionary by referring to its key name, inside square brackets:
Example
Get the value of the 'model' key:
Add Key Value Pair To Dictionary Python
Try it Yourself »There is also a method called get() that will give you the same result:
Example
Get the value of the 'model' key:
Try it Yourself »Change Values
Add To Dictionary Value Python
You can change the value of a specific item by referring to its key name:
Example
Change the 'year' to 2018:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict['year'] = 2018
Loop Through a Dictionary
You can loop through a dictionary by using a for loop.
When looping through a dictionary, the return value are the keys of the dictionary, but there are methods to return the values as well.
Example
Print all key names in the dictionary, one by one:
Try it Yourself »Example
Print all values in the dictionary, one by one:
Try it Yourself »Example
You can also use the values() function to return values of a dictionary:
Example
Loop through both keys and values, by using the items() function:
Check if Key Exists
To determine if a specified key is present in a dictionary use the in keyword:
 Resident Evil 2 Activation Key generator! Resident Evil 2Keygen is here and it is FREE and 100% working and legit. XXXXX - XXXXX - XXXXX - XXXXX - XXXXX. Resident Evil 2 Activation Key generator! Resident Evil 2Keygen is here and it is FREE and 100% working and legit.
Resident Evil 2 Activation Key generator! Resident Evil 2Keygen is here and it is FREE and 100% working and legit. XXXXX - XXXXX - XXXXX - XXXXX - XXXXX. Resident Evil 2 Activation Key generator! Resident Evil 2Keygen is here and it is FREE and 100% working and legit.
Example
Check if 'model' is present in the dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
if 'model' in thisdict:
print('Yes, 'model' is one of the keys in the thisdict dictionary')
Dictionary Length
To determine how many items (key-value pairs) a dictionary has, use the len() method.
Example
Print the number of items in the dictionary:
Try it Yourself »Adding Items
Adding an item to the dictionary is done by using a new index key and assigning a value to it:
Example
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict['color'] = 'red'
print(thisdict)
Removing Items
There are several methods to remove items from a dictionary:
Example
The pop() method removes the item with the specified key name:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.pop('model')
print(thisdict)
Example
The popitem() method removes the last inserted item (in versions before 3.7, a random item is removed instead):
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.popitem()
print(thisdict)
Example
The del keyword removes the item with the specified key name:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
del thisdict['model']
print(thisdict)
Example
The del keyword can also delete the dictionary completely:
Contact your BASIS team. For a valid SAP license, you have SAP log ID to the service market place Enter your SAP user ID; it will generate the developer access key Use this key to start you developement work. In Market Place. Go to Key & request. Choose SSCR Keys. Register developer. If the hint is useful Say thanks by reward. Sep 06, 2018 Keygen sap r3 license and object key generator v170exe developer access you will get a disclaimer about the use of hana express after read it be prompted to and key in sap easy access sap ides developer access key generator the best images. 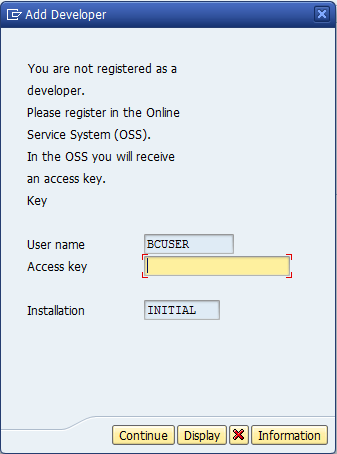 SAP Developer Key and Access Key What is Developer Key and why it is required: Whenever the ABAP developer wants to make changes to any of the SAP customized objects (i.e. The objects/programs that is there in the “Z” namespace) it require a Developer Key which is used to register user with SAP.
SAP Developer Key and Access Key What is Developer Key and why it is required: Whenever the ABAP developer wants to make changes to any of the SAP customized objects (i.e. The objects/programs that is there in the “Z” namespace) it require a Developer Key which is used to register user with SAP.
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
del thisdict
print(thisdict) #this will cause an error because 'thisdict' no longer exists.
Example
The clear() method empties the dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.clear()
print(thisdict)
Copy a Dictionary
You cannot copy a dictionary simply by typing dict2 = dict1, because: dict2 will only be a reference to dict1, and changes made in dict1 will automatically also be made in dict2.
There are ways to make a copy, one way is to use the built-in Dictionary method copy().
Example
Make a copy of a dictionary with the copy() method:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
mydict = thisdict.copy()
print(mydict)
Another way to make a copy is to use the built-in method dict().
Example
Make a copy of a dictionary with the dict() method:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
mydict = dict(thisdict)
print(mydict)
Nested Dictionaries
A dictionary can also contain many dictionaries, this is called nested dictionaries.
Example
Create a dictionary that contain three dictionaries:
'child1' : {
'name' : 'Emil',
'year' : 2004
},
'child2' : {
'name' : 'Tobias',
'year' : 2007
},
'child3' : {
'name' : 'Linus',
'year' : 2011
}
}
Or, if you want to nest three dictionaries that already exists as dictionaries:
Example
Create three dictionaries, than create one dictionary that will contain the other three dictionaries:
'name' : 'Emil',
'year' : 2004
}
child2 = {
'name' : 'Tobias',
'year' : 2007
}
child3 = {
'name' : 'Linus',
'year' : 2011
}
myfamily = {
'child1' : child1,
'child2' : child2,
'child3' : child3
}
The dict() Constructor
It is also possible to use the dict() constructor to make a new dictionary:
Example
# note that keywords are not string literals
# note the use of equals rather than colon for the assignment
print(thisdict)
Dictionary Methods
Python has a set of built-in methods that you can use on dictionaries.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all the elements from the dictionary |
| copy() | Returns a copy of the dictionary |
| fromkeys() | Returns a dictionary with the specified keys and value |
| get() | Returns the value of the specified key |
| items() | Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair |
| keys() | Returns a list containing the dictionary's keys |
| pop() | Removes the element with the specified key |
| popitem() | Removes the last inserted key-value pair |
| setdefault() | Returns the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist: insert the key, with the specified value |
| update() | Updates the dictionary with the specified key-value pairs |
| values() | Returns a list of all the values in the dictionary |
Dictionary
A dictionary is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. In Python dictionaries are written with curly brackets, and they have keys and values.
Example
Create and print a dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
print(thisdict)
Accessing Items
You can access the items of a dictionary by referring to its key name, inside square brackets:
Example
Get the value of the 'model' key:
Try it Yourself »There is also a method called get() that will give you the same result:
Example
Get the value of the 'model' key:
Try it Yourself »Change Values
You can change the value of a specific item by referring to its key name:
Example
Change the 'year' to 2018:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict['year'] = 2018
Loop Through a Dictionary
You can loop through a dictionary by using a for loop.
When looping through a dictionary, the return value are the keys of the dictionary, but there are methods to return the values as well.
Example
Print all key names in the dictionary, one by one:
Try it Yourself »Example
Print all values in the dictionary, one by one:
Try it Yourself »Example
You can also use the values() function to return values of a dictionary:
Example
Loop through both keys and values, by using the items() function:
Check if Key Exists
To determine if a specified key is present in a dictionary use the in keyword:
Example
Check if 'model' is present in the dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
if 'model' in thisdict:
print('Yes, 'model' is one of the keys in the thisdict dictionary')
Dictionary Length
To determine how many items (key-value pairs) a dictionary has, use the len() method.
Example
Print the number of items in the dictionary:
Try it Yourself »Adding Items
Adding an item to the dictionary is done by using a new index key and assigning a value to it:
Example
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict['color'] = 'red'
print(thisdict)
Removing Items
There are several methods to remove items from a dictionary:
Example
The pop() method removes the item with the specified key name:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.pop('model')
print(thisdict)
Example
The popitem() method removes the last inserted item (in versions before 3.7, a random item is removed instead):
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.popitem()
print(thisdict)
Example
The del keyword removes the item with the specified key name:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
del thisdict['model']
print(thisdict)
Example
The del keyword can also delete the dictionary completely:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
del thisdict
print(thisdict) #this will cause an error because 'thisdict' no longer exists.
Example
The clear() method empties the dictionary:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
thisdict.clear()
print(thisdict)
Copy a Dictionary
You cannot copy a dictionary simply by typing dict2 = dict1, because: dict2 will only be a reference to dict1, and changes made in dict1 will automatically also be made in dict2.
There are ways to make a copy, one way is to use the built-in Dictionary method copy().
Example
Make a copy of a dictionary with the copy() method:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
mydict = thisdict.copy()
print(mydict)
Another way to make a copy is to use the built-in method dict().
Example
Make a copy of a dictionary with the dict() method:
'brand': 'Ford',
'model': 'Mustang',
'year': 1964
}
mydict = dict(thisdict)
print(mydict)
Nested Dictionaries
A dictionary can also contain many dictionaries, this is called nested dictionaries.
Example
Create a dictionary that contain three dictionaries:
'child1' : {
'name' : 'Emil',
'year' : 2004
},
'child2' : {
'name' : 'Tobias',
'year' : 2007
},
'child3' : {
'name' : 'Linus',
'year' : 2011
}
}
Or, if you want to nest three dictionaries that already exists as dictionaries:
Example
Create three dictionaries, than create one dictionary that will contain the other three dictionaries:
'name' : 'Emil',
'year' : 2004
}
child2 = {
'name' : 'Tobias',
'year' : 2007
}
child3 = {
'name' : 'Linus',
'year' : 2011
}
myfamily = {
'child1' : child1,
'child2' : child2,
'child3' : child3
}
The dict() Constructor
It is also possible to use the dict() constructor to make a new dictionary:
Example
# note that keywords are not string literals
# note the use of equals rather than colon for the assignment
print(thisdict)
Dictionary Methods
Python has a set of built-in methods that you can use on dictionaries.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all the elements from the dictionary |
| copy() | Returns a copy of the dictionary |
| fromkeys() | Returns a dictionary with the specified keys and value |
| get() | Returns the value of the specified key |
| items() | Returns a list containing a tuple for each key value pair |
| keys() | Returns a list containing the dictionary's keys |
| pop() | Removes the element with the specified key |
| popitem() | Removes the last inserted key-value pair |
| setdefault() | Returns the value of the specified key. If the key does not exist: insert the key, with the specified value |
| update() | Updates the dictionary with the specified key-value pairs |
| values() | Returns a list of all the values in the dictionary |